Terms Used to Describe Cooling Curves
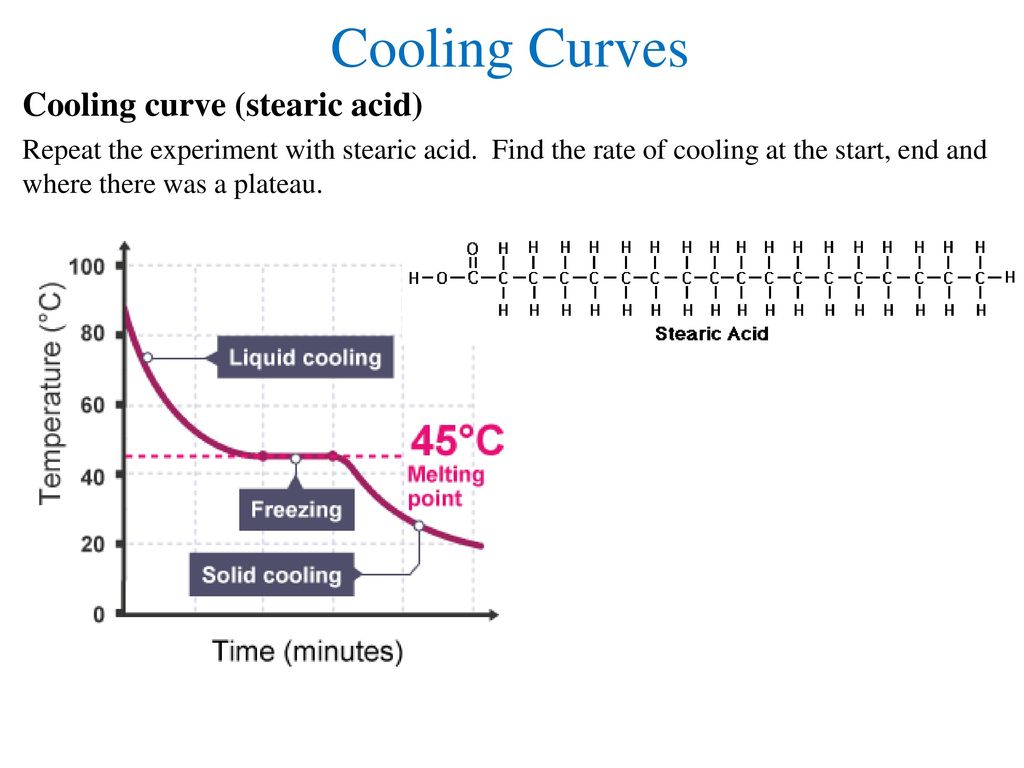
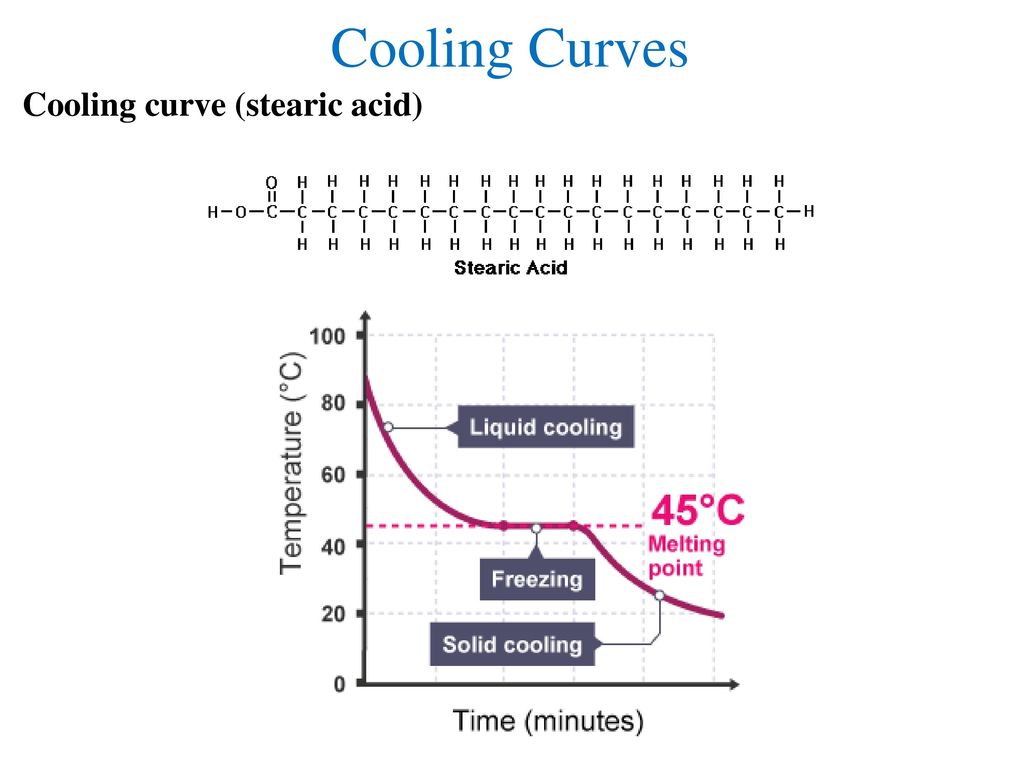
The result of the rate of cooling for stearic acid in air was 0Cper. Use the cooling curve below to answer the following questions.
Start each with water at the same temperature and record information from several sensors on the same graph.
. This standard is used extensively for the characterization of cooling curve behavior of oil quenchants. Describe how data from cooling curves can be used to construct a phase diagram. Stearic acid in air digital based thermometer.
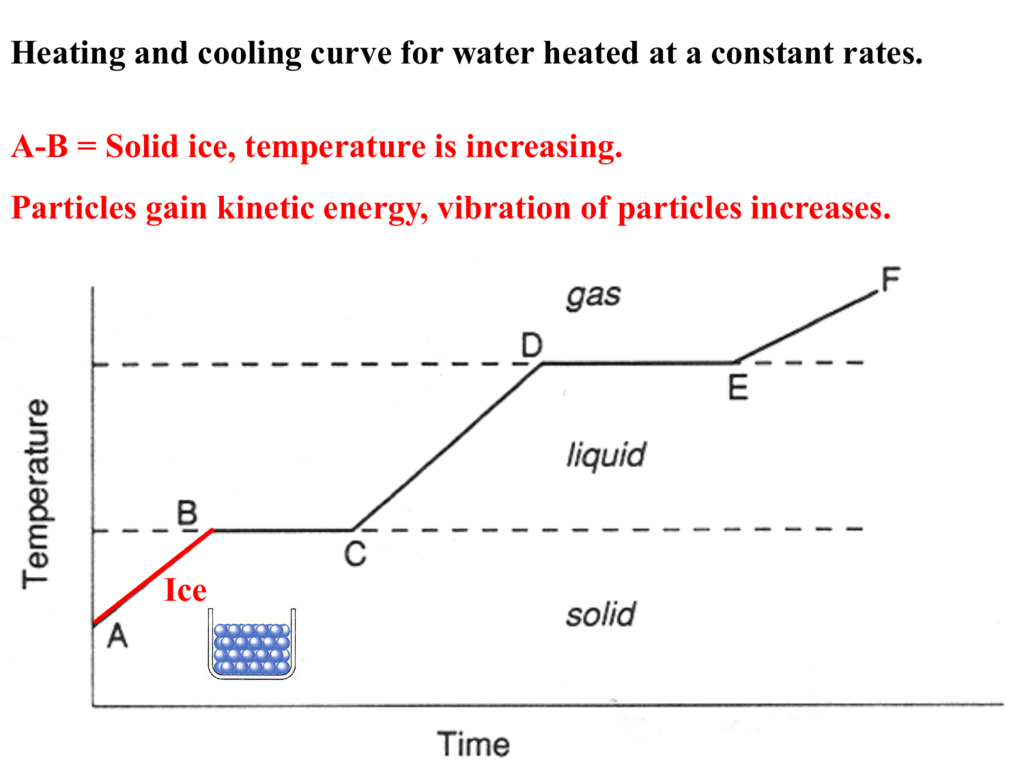
STUDY OF COOLING CURVES. A cooling curve is a line graph that represents the change of phase of matter typically from a gas to a solid or a liquid to a solid. A cooling curve is a line graph that represents the change of phase of matter typically from a gas to a solid or a liquid to a solid.
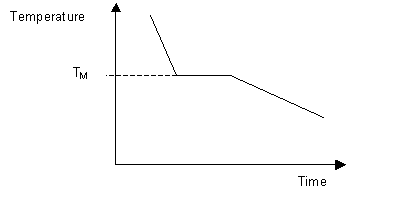
The common folk just had to live with it but royalty carried their cooling system wherever they went. The melting temperature of any pure material a one-component system at constant pressure is a single unique temperature. A substance shows which state exists at a given temperature and pressure.
There are two possibilities. Terms in this set 32 Phase Diagram. A cooling graphically shows the change in state of substances from liquid to solid.
THE HEATING CURVE OF WATER Directions. To study the cooling curve of stearic acid and its rate of cooling. 1Change in y change in x 213 7 1Cper min.
Practice personal hygiene protocols at all times Activity 2. One of the major problems was the heat. That associated with vaporizing a liquid or a solid or condensing a vapor is called the heat of vaporization.
Phase Diagram HeatingCooling Curve Vocab. Analysis of the cooling curves. The heat associated with melting a solid or freezing a liquid is called the heat of fusion.
When cooled the temperature of the molten material will steadily decrease until the melting point is. 100 1 rating Transcribed image text. You will use lauric acid in a school lab to make your own cooling curve.
A cooling curve is a type of graph used in chemistry physics engineering and other disciplines to chart the progress of a cooling substance. This problem has been solved. The representative cooling curves are shown in Figure 5.
To study the cooling curve of paraffin wax. Interpretation of cooling curves. Lauric acid has a.
Life in the desert was difficult for the ancient Egyptians. The independent variable X-axis is time and the dependent variable Y-axis is temperature. Compare cooling curves for beakers with different insulation lids etc.
HEATING AND COOLING CURVES Activity 1. Fan bearers were available to wave fans make a breeze and cool the sweaty brow of the aristocrats. All the cooling curves show similar responses.
Heat a substance and measure its temperature for. To find out the accuracy of the thermometers. A cooling curve is a line graph that represents the change of phase of matter typically from a gas to a solid or a liquid to a solid.
The sample is allowed to cool undisturbed ie without having the aluminum placed in it. THE COOLING CURVE OF WATER Directions. Data from the cooling curve can be used to determine if the oils meet new manufacturing specifications for the quenchant.
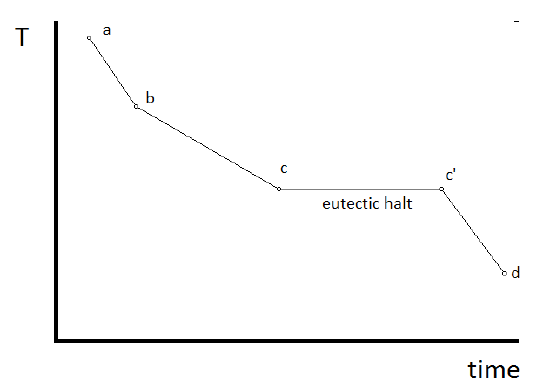
Represents the temperature and pressure where all three states of matter coexist. The differential curve dTdt versus time t is used by Backerud and others to show how the area between the cooling curve and the baseline can yield the heat evolved during the formation of that particular phase that is solidifying at the time. A cooling curve of naphthalene from liquid to solid.
The term _____ is used to describe how well the electron cloud around an atom responds to changes in its electronic environment. This calibration curve is ob-tained using an identical sample of initially hot water. These are mirror images of the heating curve.
The liquid and solid phases exist together in equilibrium only at this temperature. The independent variable X-axis is time and the dependent variable Y-axis is temperature. Comparison of cooling curves for the same oil from four different customers compared to new oil control.
1 it ex-tends through the transition region and thus re-. A cooling curve is a line graph that represents the change of phase of matter typically from either a gas to a solid or a liquid to a solidTime is used in the x-axis while temperature is used for the y-axis. When this second cooling curve is superimposed on the upper portion of the curve in Fig.
Below is an example of a cooling curve used in castings. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Changes of state can be investigated by measuring the temperature as a substance changes state.
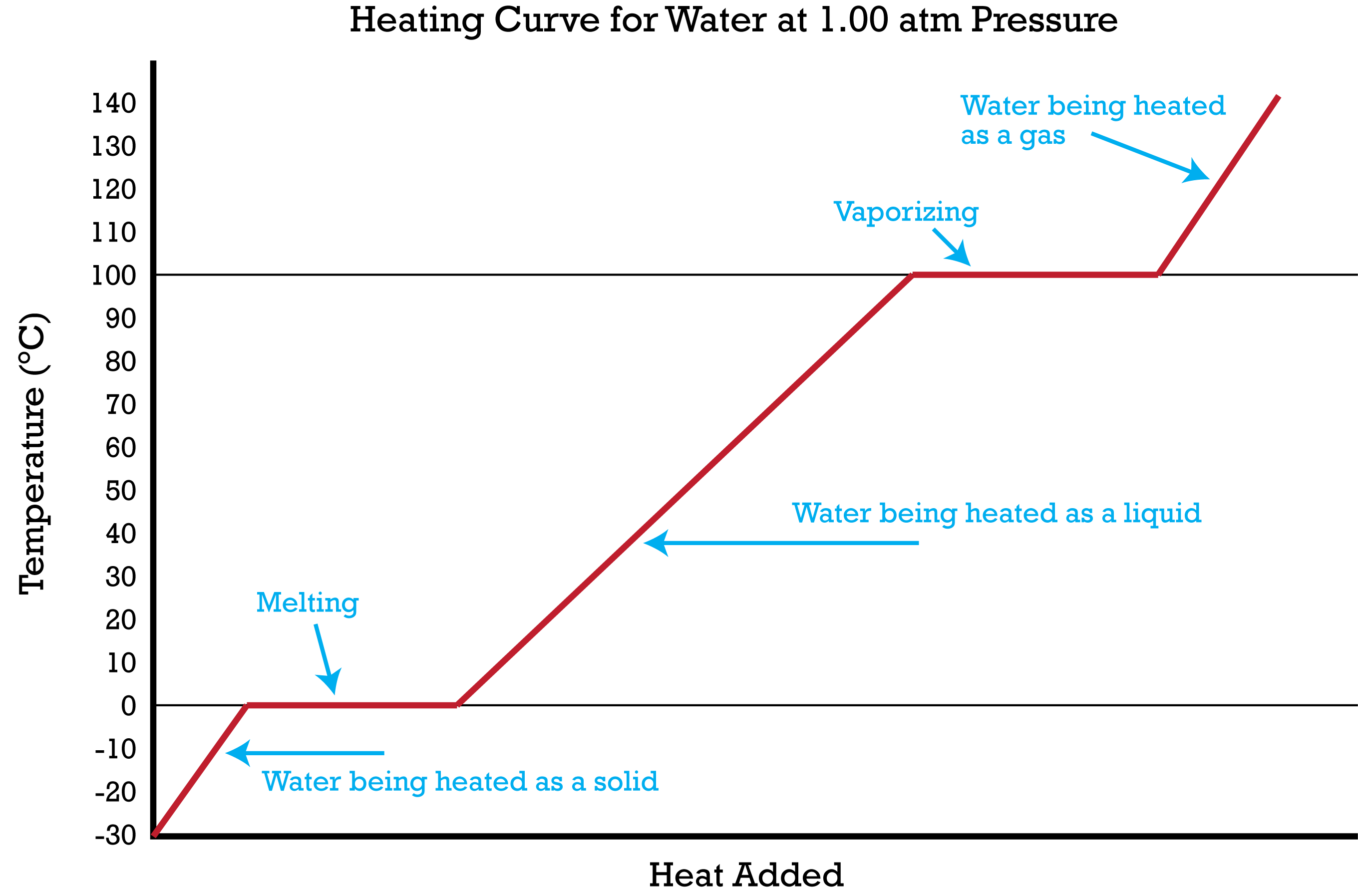
As such a cooling curve generally slopes downward from left to right as the temperature decreases over time. Using the curve below describe what is happening between each of the points. A heating or cooling curve is a simple line graph that shows the phase changes a given substance undergoes with increasing or decreasing temperature.
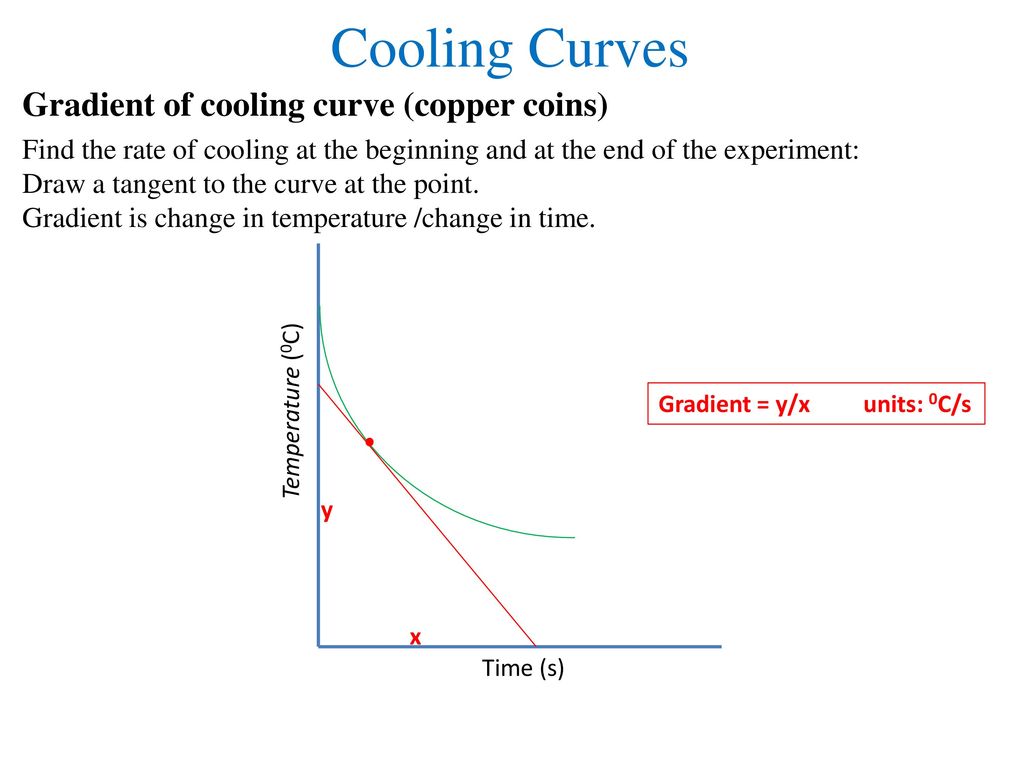
The cooling rate is the slope of the cooling curve at any point. If I have one mole of a solid compound what is the term used to describe how much heat is needed to melt it. This is the first graph shown above with.
It is used to determine the suitability of a quenchant for a particular application and is increasingly used as a. One axis of graph usually the x axis charts time while temperature is represented on the other axis. They are often used in chemistry and physics and can apply misleadingly to matter behaviour during heating as well as during.
Place sensors and heaters in beakers with 1 litre water and 250 ml. Heating curves cooling curves have horizontal flat parts where the state changes from gas to liquid or from liquid to solid. In the United States the most commonly used method for deter-mining cooling curves is ISO 9950 7 or ASTM D6200 3.
The independent variable X-axis is time and the dependent variable Y-axis is temperature. Describe how data from cooling curves can be used to construct a phase diagram. A heating cooling curve shows the changes that occurs when ____ is added to or removed from a sample of matter at a _____ rate.
A Useful Wet Blanket.

Interpretation Of Cooling Curves

Schematic Cooling Curve For Alloy Solidification Download Scientific Diagram
Cooling Curves Aim Investigate Cooling Of Different Substances And Use The Data Obtained From These Experiments To Construct Cooling Curves Where The Rate Ppt Download

3 Cooling Curve For A Pure Metal Download Scientific Diagram
Practical Maintenance Blog Archive I T Diagram And Cooling Curves

What Are Heating And Cooling Curves Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

The Graph To The Right Shows A Cooling Curve For Stearic Acid Stearic
Cooling Curves Aim Investigate Cooling Of Different Substances And Use The Data Obtained From These Experiments To Construct Cooling Curves Where The Rate Ppt Download

Heating And Cooling Curves Overview Examples Expii
8 10 Cooling Curves Chemistry Libretexts
Cooling Curves Aim Investigate Cooling Of Different Substances And Use The Data Obtained From These Experiments To Construct Cooling Curves Where The Rate Ppt Download

3 Cooling Curve For A Pure Metal Download Scientific Diagram

Cooling Curves Of Hot Water And Cold Water The Same Amount Of Water Download Scientific Diagram
Heating And Cooling Curves Read Chemistry Ck 12 Foundation

Heating Curve And Cooling Curve Of Water Enthalpy Of Fusion Vaporization Youtube

What Are Heating And Cooling Curves Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Heating And Cooling Curves Overview Examples Expii

Schematic Cooling Curve For Alloy Solidification Download Scientific Diagram

Comments
Post a Comment